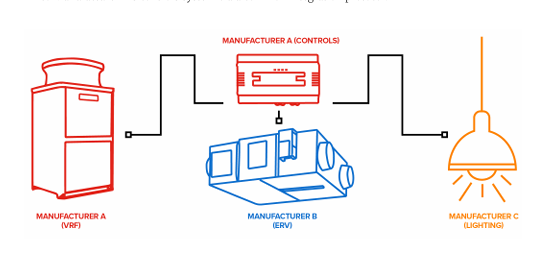
VRF Integration with BMS system
VRF HVAC System:
- Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) system is a type of HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) technology that uses refrigerant as the cooling and heating medium. It is characterized by the ability to vary the flow of refrigerant to indoor units based on the precise demand of different zones within a building.
- A VRF system includes of an outside compressor, multiple indoor evaporator units and refrigerant pipes to connect them. This design enables maximum flexibility and customization control for each indoor unit.
- VRF systems incorporate complex control systems that provide reliable temperature adjustment, remote monitoring, and communication with building management systems (BMS).
VRF System Integrated with Building Management System (BMS):
- When integrating the BMS with the VRF system, they function as closed systems, limiting communication exclusively within their internal networks. Commands can solely be transmitted and received through the native control features provided by the VRF manufacturer. As a result, these systems are unable to communicate externally without the use of an additional device.
- This challenge creates a significant hurdle for integrating VRF HVAC systems into a building management system.
- This is where Cool-Master Net comes in. Since Cool Automation works directly with both BMS and VRF manufacturers, Cool Master Net can provide native-like integration for any VRF system with almost any BMS main controller.
- Cool-Master Net is an advanced HVAC control system designed to optimize the management of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems within buildings. It integrates various components of HVAC infrastructure into a unified platform, allowing for centralized monitoring and control.
- Cool-Master Net functions by connecting with different HVAC equipment such as air conditioners, heat pumps, and ventilation units through its network. It gathers real-time data on operating conditions, energy usage, and performance metrics from these devices.
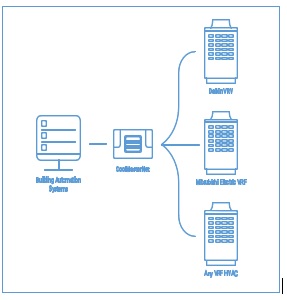
- Additionally, since Cool-Master Net’s function is to provide external access to the VRF system, it is also an essential tool to provide access to the BMS cloud-based remote-control application.
- Cool-Master Net’s advanced technologies can read the specific internal address asigned by the VRF system for each indoor unit.
- Cool Master Net will then automatically identify those units through the Home Automation System, and provide the integrator with quick and easy access to each unit through the main controller.
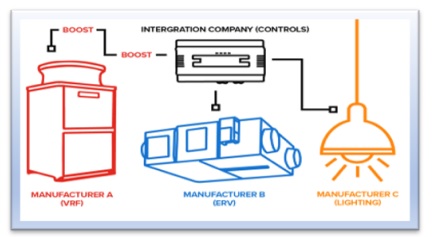
- This functionality provides simple and intuitive management for the entire system both locally as well as remotely.
- Simply, Cool Master Net is an all-in-one solution for VRF and BMS integration. It is simple to install, easy to configure and operates within the system while remaining unseen in the background.
Benefits:
Integrating Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) systems with a Building Management System (BMS) can offer numerous benefits, including:
- Centralized Control: Enables centralized monitoring and control of all HVAC equipment including VRF systems from a single interface.
- Energy Efficiency: Optimizes energy use through coordinated operation and scheduling of VRF units based on building occupancy and load conditions.
- Improved Comfort: Provides better indoor climate control by synchronizing VRF operation with other building systems like ventilation and lighting.
- Remote Monitoring: Facilitates remote monitoring of VRF system performance, allowing for proactive maintenance and troubleshooting.
- Data Analytics: Collects and analyzes data from VRF systems to identify trends, optimize settings, and improve overall system efficiency.
- Fault Detection: Enables early detection of faults or abnormalities in VRF operation, reducing downtime and enhancing reliability.
- Integration with Building Systems: Integrates seamlessly with other building systems such as fire alarms, security systems, and occupancy sensors for coordinated responses.
- Cost Savings: Helps in reducing operational costs through efficient energy management and predictive maintenance.
- Scalability: Supports scalability by accommodating future expansions or modifications in building layouts and HVAC requirements.
- Compliance and Reporting: Facilitates compliance with energy efficiency regulations and provides detailed reporting on system performance and energy usage.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, integrating a Variable Refrigerant Flow (VRF) system with a Building Management System (BMS) provides an advanced approach to HVAC control for modern buildings. This synchronization not only centralizes control and monitoring, but it further enhances energy efficiency by optimizing the performance of VRF units incorporating real-time data and building occupancy. Buildings that utilize a BMS can save costs by reducing energy use and doing preventative maintenance. In addition, the seamless coordination of VRF systems with other building systems, such as lighting and occupancy sensors, ensures increased occupant comfort and effective operation. As buildings aim for improved environmental sustainability and performance, the integration of VRF systems with BMS stands out as an essential step toward obtaining these objectives, enabling full control and more reliability.
References:
- Mitsubishi Electric Trane HVAC US white paper “APPLYING VRF AND THIRD-PARTY HVAC SYSTEMS”
- Carrier commercial white paper “integrating VRF system for improved efficiency and comfort. https://www.shareddocs.com/hvac/docs/1001/Public/07/ENG_NEWS_2_2.pdf
- Cool Automation “How VRF HVAC integrates with home automation”
https://coolautomation.com/blog/how-vrf-hvac-integrates-with-home-automation/
- Cool automation “case studies of cool Master Net”
https://coolautomation.com/products/coolmasternet/
- Mitsubishi Electric white paper “VRF and building integrations – options and how to choose among them”